The fourth act of worship is the performing of the Hajj or Pilgrimage to Mecca and it is obligatory upon every such Muslim adult (at least once in his/her lifetime) who can afford to undertake the journey and has safe access to Mecca (3:98). The time appointed for the Hajj is fixed ten weeks after Eid-ul-Fitr. Thus it starts on the eighth and continues up to the thirteenth of the lunar month of Dhul-Hijjah.
This pilgrimage to Mecca is associated with the sacrifices performed by the prophet Abraham, may peace be upon him, his wife Hagar, may peace be upon her, and his son Ishmael, may peace be upon him. With Hajj are also associated the holy traditions of the early sufferings and sacrifices of the Holy Prophet Muhammad, may peace and blessings of Allah be upon him. It offers a golden opportunity to the Muslims of different countries and diverse races to meet and discuss matters of mutual and international interest.
The Holy Ka’aba
The Ka’aba, is the focal point of Hajj, and is the first place ever to be set up in the world for the worship of Allah (4:97). It was rebuilt by the prophets Abraham and Ishmael, may peace be upon them both, some four thousand years ago. Muslims all over the world face the Ka’aba when they offer their prayers.
Various ceremonies of Hajj are summarised below:
Ihram and Talbiyah
The Hajj starts when the pilgrims reach certain designated places close to Mecca. The male pilgrims enter the state of Ihram by wearing only two seamless white sheets, and recite Talbiyah, whilst the female pilgrims are fully clothed and also recite the Talbiyah, which consists of saying the following aloud:
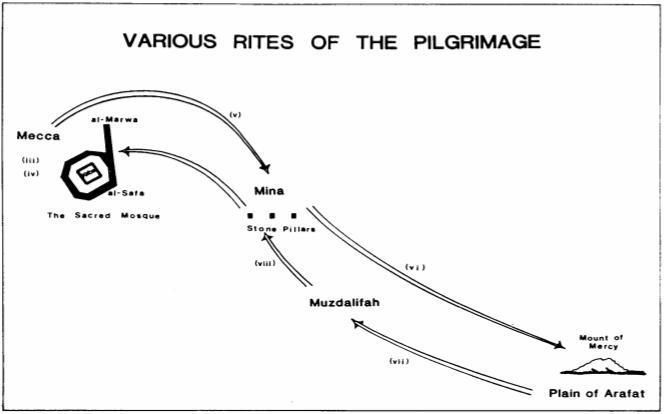
Tawaf of the Ka’aba and Sa’ee between Safa and Marwah
The pilgrims then perform the Tawaf of the Ka’aba by going around it seven times, starting from the position of the Black Stone, in an anti-clockwise direction. Next, they perform the Sa’ee by running between the hillocks of Safa and Marwah located near the Ka’aba, in memory of Hazrat Hagar, may peace be upon her, who ran in search of water in this place.
From Mecca they move to Mina, a plain four miles east of Mecca. Next morning after Fajr prayer, they leave for ‘Arafaat.
Stay at the Plain of ‘Arafaat
They worship during their stay at ‘Arafaat from the afternoon of the 9th Dhul Hijjah to the sunset. This is the place where the Holy Prophet Muhammad, may peace and blessing of Allah be upon him, delivered his Farewell Sermon. On the way back to Mecca they worship at Muzdalifah, and then stay at Mina on the 10th of Dhul Hijjah.
Stay at Mina
The pilgrims stay at Mina on the tenth day of Dhul Hijjah, where at first they perform the ceremony of Rami, a symbolic act to strike the devil by throwing seven small stones at three pillars.
Next, the pilgrims sacrifice their animals, then the men shave their heads or cut their hair short and women cut a few hairs and end the state of Ihram by wearing normal dress. On this day, the Muslims all over the world, except the pilgrims, celebrate Eid ul Adhia. On the 10th, 11th or 12th days of Dhul Hijjah, the pilgrims can perform Tawaf and Sa’ee for the second time at Mecca and once again return to Mina.
Farewell Tawaf at Mecca and the End of Hajj
After passing some days at Mina, the pilgrims return to Mecca on the 12th or the 13th of Dhul Hijjah, and perform the farewell Tawaf of the Ka’aba, which marks the completion of Hajj.
Umra
Whereas the Hajj may be performed during the prescribed dates only, ’Umra or Lesser Pilgrimage may be done at any time during the year. This also involves the state of Ihram, Tawaf of Ka’aba and Sa’ee between the hillocks of Safa and Marwah.